- Immersive experience
- Incorporating physics of material behavior
- Conversational AI
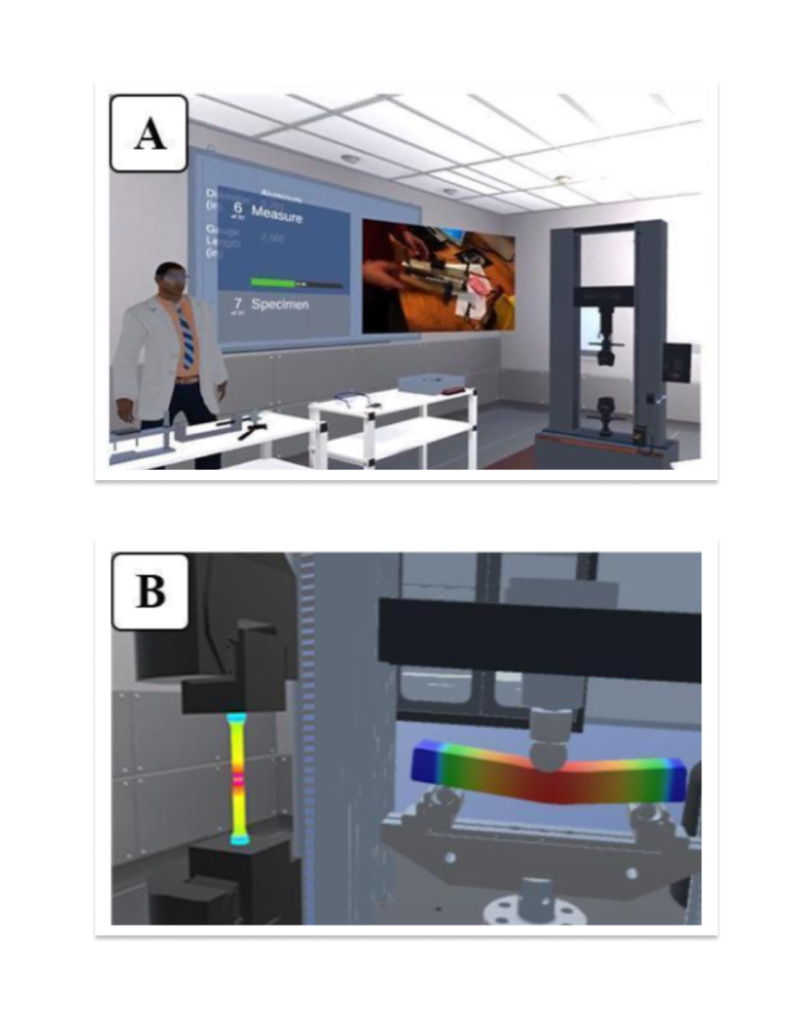
- Eliminating the safety risks, equipment availability bottlenecks and costly damage risks
- Increase student engagement
- Improve learning outcomes
- An immersive approach to virtual labs – with an emphasis on providing engagement and experiential learning
- Randomized controlled trial (RCT) based evaluation – which aims to rigorously assess the impact of interventions in human subject studies
- Innovative authoring software for immersive training – called HyperSkill to enable faculty and other subject matter experts to create their own immersive content.
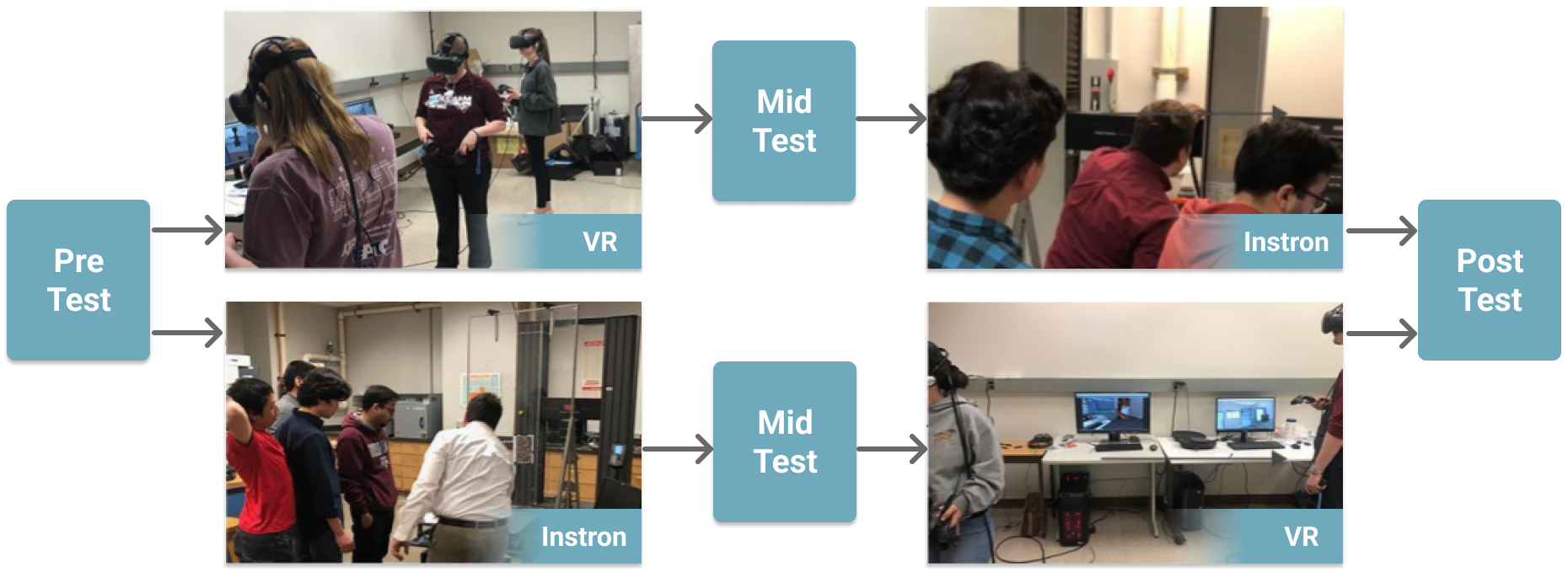
- A two-group, randomized control trial was conducted as part of a course with a total of 118 students.
- 57 participants were assigned to the control condition (Instron machine is used first, followed by VR) and 61 to the experimental condition (VR first, then Instron).
- Results of the pilot test suggested an overall positive outcome for students participating in the VR virtual lab first (experimental condition) compared to those who performed the physical lab first (control condition).
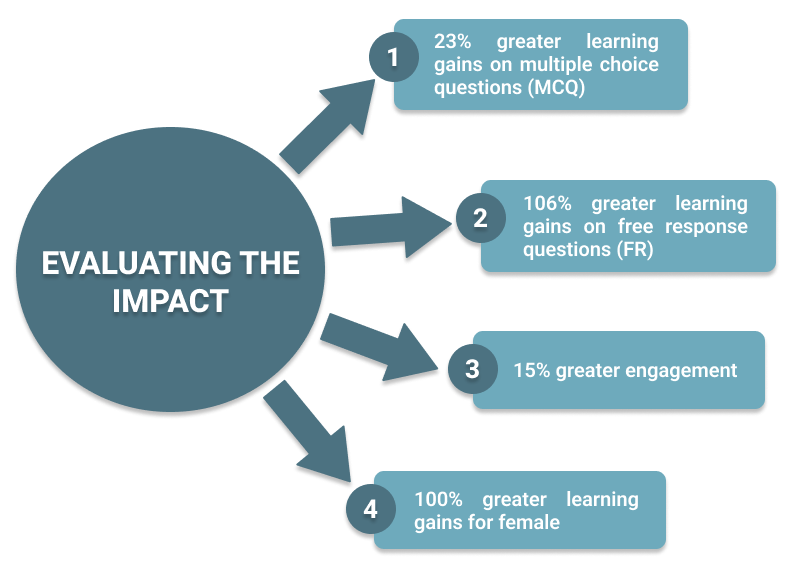
- 23% greater learning gains on multiple choice questions (MCQ) – Students who participated in the VR activity first scored 23% higher on MCQ subject matter scores, including 5% higher procedural subscale and 49% higher conceptual subscales scores.
- 106% greater learning gains on free response questions (FR) – Analysis of pre-post gain indicated significantly higher gains for participants in the VR activity compared to the Instron activity.
- 15% greater engagement – Additionally, students reported significantly higher engagement after the VR activity than after the physical lab.
- 100% greater learning gains for female participants – Subgroup analysis of pre-post learning gains indicated that females in the experimental group gained twice as much over males.